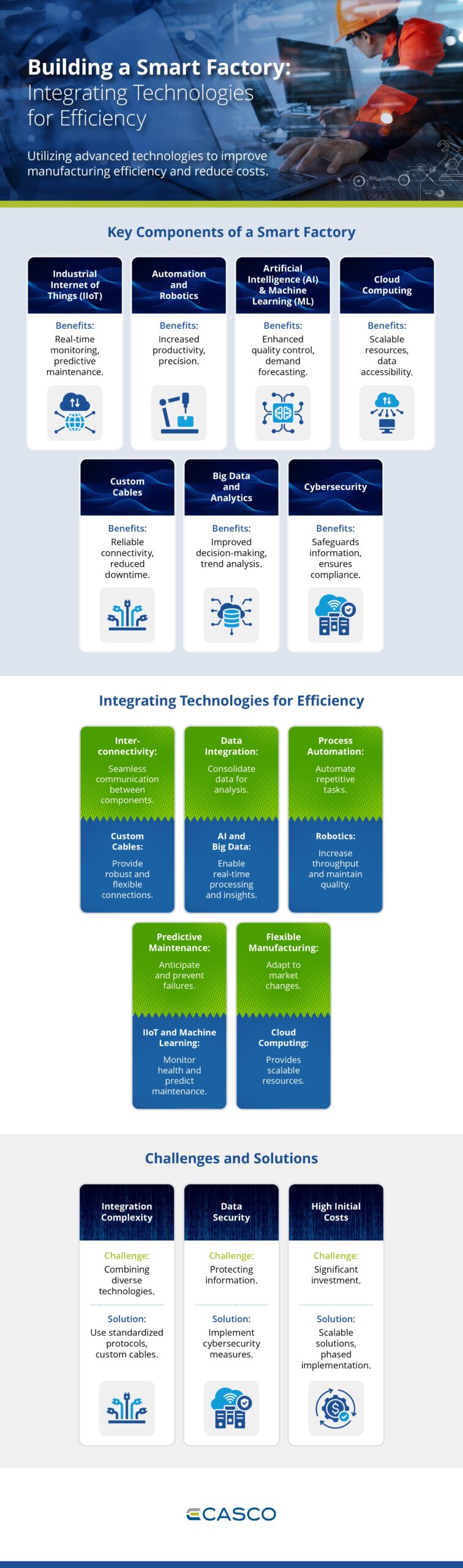
Building a smart factory revolves around utilizing cutting-edge technology to revolutionize manufacturing processes, increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance overall productivity. Today, we’ll explore how a smart factory operates by using connected systems, data analysis, automation, and artificial intelligence (AI) to create a responsive and adaptive production environment.
To start, let’s consider the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). IIoT links devices through the internet, enabling real-time data sharing and monitoring. These systems track various factors, from machine performance to environmental conditions, providing valuable insights for decision-making. With IIoT, potential maintenance issues can be predicted in advance, helping to prevent equipment failures before they occur.
Automation and robotics play a crucial role in smart factories. By taking over repetitive and hazardous tasks, robots create a safer and more efficient work environment. With precision handling and the ability to work with complex operations, automation helps produce higher-quality products and allows manufacturers to swiftly adapt to market changes.
Machine learning (ML) takes this further by analyzing vast quantities of data to fine-tune processes. ML can detect patterns and trends, enabling manufacturers to better predict demand and make adjustments to production schedules. This technology ensures processes are continuously optimized over time, resulting in smoother and more efficient operations.
Cloud computing is also a significant piece of the puzzle. It provides scalable solutions for data storage and processing, allowing critical data to be accessed from anywhere. This capability facilitates real-time decision-making and cuts costs by reducing the need for extensive on-site IT infrastructure.
Dependable connectivity is vital in smart factories, and custom cable assembly manufacturers play an important role by supplying tailored, reliable connections to meet specific needs. Using custom cable assemblies reduces downtime and enhances system communication efficiency, contributing to the overall productivity of the factory.
Data analytics is another key factor in driving smart factory success. By analyzing large data sets, manufacturers can discover ways to optimize workflows, identify inefficiencies, and predict future performance. This level of insight enables better decision-making and contributes to increased productivity.
Lastly, cybersecurity is a growing concern in smart manufacturing. With more systems and devices connected, smart factories are more vulnerable to security breaches. Strong security measures, including encryption and monitoring, are essential to maintain operational integrity and safeguard critical factory systems.